Publications & Posters
CellSighter: a neural network to classify cells in highly multiplexed images<span class='publication-meta'>Amitay, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Nat. Comm.</i> July 2023</span>
Multiplexed imaging enables measurement of multiple proteins in situ, offering an unprecedented opportunity to chart various cell types and states in tissues. However, cell classification, the task of identifying the type of individual cells, remains challenging, labor-intensive, and limiting to throughput. Here, we present CellSighter, a deep-learning based pipeline to accelerate cell classification in multiplexed images. Given a small training set of expert-labeled images, CellSighter outputs the label probabilities for all cells in new images. CellSighter achieves over 80% accuracy for major cell types across imaging platforms, which approaches inter-observer concordance. Ablation studies and simulations show that CellSighter is able to generalize its training data and learn features of protein expression levels, as well as spatial features such as subcellular expression patterns. CellSighter’s design reduces overfitting, and it can be trained with only thousands or even hundreds of labeled examples. CellSighter also outputs a prediction confidence, allowing downstream experts control over the results. Altogether, CellSighter drastically reduces hands-on time for cell classification in multiplexed images, while improving accuracy and consistency across datasets.
Amitay, et al., Nat. Comm. July 2023
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40066-7
Expanded vacuum-stable gels for multiplexed high-resolution spatial histopathology<span class='publication-meta'>Bai, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Nat. Comm.</i> July 2023</span>
Cellular organization and functions encompass multiple scales in vivo. Emerging high-plex imaging technologies are limited in resolving subcellular biomolecular features. Expansion Microscopy (ExM) and related techniques physically expand samples for enhanced spatial resolution, but are challenging to be combined with high-plex imaging technologies to enable integrative multiscaled tissue biology insights. Here, we introduce Expand and comPRESS hydrOgels (ExPRESSO), an ExM framework that allows high-plex protein staining, physical expansion, and removal of water, while retaining the lateral tissue expansion. We demonstrate ExPRESSO imaging of archival clinical tissue samples on Multiplexed Ion Beam Imaging and Imaging Mass Cytometry platforms, with detection capabilities of > 40 markers. Application of ExPRESSO on archival human lymphoid and brain tissues resolved tissue architecture at the subcellular level, particularly that of the blood-brain barrier. ExPRESSO hence provides a platform for extending the analysis compatibility of hydrogel-expanded biospecimens to mass spectrometry, with minimal modifications to protocols and instrumentation.
Bai, et al., Nat. Comm. July 2023
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-39616-w
Spatial profiling technologies illuminate the tumor microenvironment<span class='publication-meta'>Elhanani, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Cancer Cell</i> March 2023</span>
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is composed of many different cellular and acellular components that together drive tumor growth, invasion, metastasis, and response to therapies. Increasing realization of the significance of the TME in cancer biology has shifted cancer research from a cancer-centric model to one that considers the TME as a whole. Recent technological advancements in spatial profiling methodologies provide a systematic view and illuminate the physical localization of the components of the TME. In this review, we provide an overview of major spatial profiling technologies. We present the types of information that can be extracted from these data and describe their applications, findings and challenges in cancer research. Finally, we provide a future perspective of how spatial profiling could be integrated into cancer research to improve patient diagnosis, prognosis, stratification to treatment and development of novel therapeutics.
Elhanani, et al., Cancer Cell March 2023
doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2023.01.010
Diffuse large B-cell lymphomas have spatially defined, tumor immune microenvironments revealed by high-parameter imaging <span class='publication-meta'>Wright, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Blood Adv.</i> March 2023</span>
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified is the most common aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma and a biologically heterogeneous disease. Despite the development of effective immunotherapies, the organization of the DLBCL tumor-immune microenvironment (TIME) remains poorly understood.We interrogated the intact TIME of 51 de novo DLBCLs with triplicate sampling to characterize 337 995 tumor and immune cells using a 27-plex antibody panel that captured cell lineage, architectural, and functional markers. We spatially assigned individual cells, identified local cell neighborhoods, and established their topographical organization in situ. We found that the organization of local tumor and immune cells can be modeled by 6 composite cell neighborhood types (CNTs). Differential CNT representation divided cases into 3 aggregate TIME categories: immune-deficient, dendritic cell–enriched (DC-enriched), and macrophage-enriched (Mac-enriched). Cases with immune-deficient TIMEs have tumor cell–rich CNTs, in which the few infiltrating immune cells are enriched near CD31+ vessels, in keeping with limited immune activity. Cases with DC-enriched TIMEs selectively include tumor cell–poor/immune cell–rich CNTs with high numbers of CD11c+ DCs and antigen-experienced T cells also enriched near CD31+ vessels, in keeping with increased immune activity. Cases with Mac-enriched TIMEs selectively include tumor cell–poor/immune cell–rich CNTs with high numbers of CD163+ macrophages and CD8 T cells throughout the microenvironment, accompanied by increased IDO-1 and LAG-3 and decreased HLA-DR expression and genetic signatures in keeping with immune evasion. Our findings reveal that the heterogenous cellular components of DLBCL are not randomly distributed but organized into CNTs that define aggregate TIMEs with distinct cellular, spatial, and functional features.
Key Points:
- DLBCLs are composed of local cell neighborhoods with distinct cellular, spatial, and functional features that define structured TIMEs.
- DLBCL cell neighborhoods structurally define immune-deficient, DC-enriched, and macrophage-enriched immune microenvironments.
Wright, et al., Blood Adv. March 2023
doi: https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2023009813
MAPS: Pathologist-level cell type annotation from tissue images through machine learning<span class='publication-meta'>Shaban, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Biorxiv</i>, 2023</span>
Highly multiplexed protein imaging is emerging as a potent technique for analyzing protein distribution within cells and tissues in their native context. However, existing cell annotation methods utilizing high-plex spatial proteomics data are resource intensive and necessitate iterative expert input, thereby constraining their scalability and practicality for extensive datasets. We introduce MAPS (Machine learning for Analysis of Proteomics in Spatial biology), a machine learning approach facilitating rapid and precise cell type identification with human-level accuracy from spatial proteomics data. Validated on multiple in-house and publicly available MIBI and CODEX datasets, MAPS outperforms current annotation techniques in terms of speed and accuracy, achieving pathologist-level precision even for challenging cell types, including tumor cells of immune origin. By democratizing rapidly deployable and scalable machine learning annotation, MAPS holds significant potential to expedite advances in tissue biology and disease comprehension.
Shaban, et al., Biorxiv, 2023
doi: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.06.25.546474v1
Dynamic CD8+ T cell responses to cancer immunotherapy in human regional lymph nodes are disrupted in metastatic lymph nodes<span class='publication-meta'>Rahim, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Cell</i> March 2023</span>
Abstract:
CD8+ T cell responses are critical for anti-tumor immunity. While extensively profiled in the tumor microenvironment, recent studies in mice identified responses in lymph nodes (LNs) as essential; however, the role of LNs in human cancer patients remains unknown. We examined CD8+ T cells in human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas, regional LNs, and blood using mass cytometry, single-cell genomics, and multiplexed ion beam imaging. We identified progenitor exhausted CD8+ T cells (Tpex) that were abundant in uninvolved LN and clonally related to terminally exhausted cells in the tumor. After anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy, Tpex in uninvolved LNs reduced in frequency but localized near dendritic cells and proliferating intermediate-exhausted CD8+ T cells (Tex-int), consistent with activation and differentiation. LN responses coincided with increased circulating Tex-int. In metastatic LNs, these response hallmarks were impaired, with immunosuppressive cellular niches. Our results identify important roles for LNs in anti-tumor immune responses in humans.
Highlights:
- Tpex are abundant in uiLNs and clonally related to Tex-term in the TME
- After anti-PD-L1 treatment, activated Tpex and Tex-int localize near DCs in uiLNs
- uiLN anti-PD-L1 responses coincide with increased circulating Tex-int
- Tpex and Tex-int responses to anti-PD-L1 therapy are disrupted in metLNs
Rahim, et al., Cell March 2023
doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2023.02.021
DCIS genomic signatures define biology and correlate with clinical outcome: a Human Tumor Atlas Network (HTAN) analysis of TBCRC 038 and RAHBT cohorts<span class='publication-meta'>Strand, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Cancer Cell</i> November 2022</span>
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is the most common precursor of invasive breast cancer (IBC), with variable propensity for progression. We perform multiscale, integrated molecular profiling of DCIS with clinical outcomes by analyzing 774 DCIS samples from 542 patients with 7.3 years median follow-up from the Translational Breast Cancer Research Consortium 038 study and the Resource of Archival Breast Tissue cohorts. We identify 812 genes associated with ipsilateral recurrence within 5 years from treatment and develop a classifier that predicts DCIS or IBC recurrence in both cohorts. Pathways associated with recurrence include proliferation, immune response, and metabolism. Distinct stromal expression patterns and immune cell compositions are identified. Our multiscale approach employed in situ methods to generate a spatially resolved atlas of breast precancers, where complementary modalities can be directly compared and correlated with conventional pathology findings, disease states, and clinical outcome.
Highlights:
- Development of a new classifier for DCIS recurrence or progression
- Four stroma-specific signatures identified
- Outcome-associated pathways identified across multiple data types and compartments
- CNAs characterize DCIS subgroups associated with high-risk invasive cancers
Strand, et al., Cancer Cell November 2022
doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2022.10.021
Spatial epitope barcoding reveals subclonal tumor patch behaviors<span class='publication-meta'>Rovira-Clavé, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Cancer Cell</i> November 2022</span>
Abstract: Intratumoral heterogeneity is a seminal feature of human tumors contributing to tumor progression and response to treatment. Current technologies are still largely unsuitable to accurately track phenotypes and clonal evolution within tumors, especially in response to genetic manipulations. Here, we developed epitopes for imaging using combinatorial tagging (EpicTags), which we coupled to multiplexed ion beam imaging (EpicMIBI) for in situ tracking of barcodes within tissue microenvironments. Using EpicMIBI, we dissected the spatial component of cell lineages and phenotypes in xenograft models of small cell lung cancer. We observed emergent properties from mixed clones leading to the preferential expansion of clonal patches for both neuroendocrine and non-neuroendocrine cancer cell states in these models. In a tumor model harboring a fraction of PTEN-deficient cancer cells, we observed a non-autonomous increase of clonal patch size in PTEN wild-type cancer cells. EpicMIBI facilitates in situ interrogation of cell-intrinsic and cell-extrinsic processes involved in intratumoral heterogeneity.
Rovira-Clavé, et al., Cancer Cell November 2022
doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2022.09.014
Single-cell spatial proteomic imaging for human neuropathology <span class='publication-meta'>Vijayaragavan & Cannon, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Acta Neuropathol Commun</i> November 2022</span>
Abstract: Neurodegenerative disorders are characterized by phenotypic changes and hallmark proteopathies. Quantifying these in archival human brain tissues remains indispensable for validating animal models and understanding disease mechanisms. We present a framework for nanometer-scale, spatial proteomics with multiplex ion beam imaging (MIBI) for capturing neuropathological features. MIBI facilitated simultaneous, quantitative imaging of 36 proteins on archival human hippocampus from individuals spanning cognitively normal to dementia. Customized analysis strategies identified cell types and proteopathies in the hippocampus across stages of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) neuropathologic change. We show microglia-pathologic tau interactions in hippocampal CA1 subfield in AD dementia. Data driven, sample independent creation of spatial proteomic regions identified persistent neurons in pathologic tau neighborhoods expressing mitochondrial protein MFN2, regardless of cognitive status, suggesting a survival advantage. Our study revealed unique insights from multiplexed imaging and data-driven approaches for neuropathologic analysis and serves broadly as a methodology for spatial proteomic analysis of archival human neuropathology.
Vijayaragavan, K. & Cannon, B.J., et al., Acta Neuropathologica Communications Nov 2022
doi: https://www.ionpath.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Ionpath-MIBI-Oveview-221109.pdf
Single-nucleus and spatial transcriptomics of archival pancreatic cancer reveals multi-compartment reprogramming after neoadjuvant treatment<span class='publication-meta'>Hwang, <i>et al., Nature Genetics</i> July 2022</span>
Hwang, et al., Nature Genetics July 2022
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-022-01134-8
An approach that combines protein and nucleic acid imaging reveals virus-dependent B cell and macrophage immunosuppression of tissue microenvironments <span class='publication-meta'>Jiang, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Immunity</i> April 2022</span>
Abstract: Understanding the mechanisms of HIV tissue persistence necessitates the ability to visualize tissue microenvironments where infected cells reside; however, technological barriers limit our ability to dissect the cellular components of these HIV reservoirs. Here, we developed protein and nucleic acid in situ imaging (PANINI) to simultaneously quantify DNA, RNA, and protein levels within these tissue compartments. By coupling PANINI with multiplexed ion beam imaging (MIBI), we measured over 30 parameters simultaneously across archival lymphoid tissues from healthy or simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV)-infected nonhuman primates. PANINI enabled the spatial dissection of cellular phenotypes, functional markers, and viral events resulting from infection. SIV infection induced IL-10 expression in lymphoid B cells, which correlated with local macrophage M2 polarization. This highlights a potential viral mechanism for conditioning an immunosuppressive tissue environment for virion production. The spatial multimodal framework here can be extended to decipher tissue responses in other infectious diseases and tumor biology.
Jiang, et al., Immunity April 2022
doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2022.03.020
Reproducible, high-dimensional imaging in archival human tissue by Multiplexed Ion Beam Imaging by Time-of-Flight (MIBI-TOF) <span class='publication-meta'>Liu, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Lab. Invest.</i> March 2022</span>
Abstract: Multiplexed ion beam imaging by time-of-flight (MIBI-TOF) is a form of mass spectrometry imaging that uses metal labeled antibodies and secondary ion mass spectrometry to image dozens of proteins simultaneously in the same tissue section. Working with the National Cancer Institute’s (NCI) Cancer Immune Monitoring and Analysis Centers (CIMAC), we undertook a validation study, assessing concordance across a dozen serial sections of a tissue microarray of 21 samples that were independently processed and imaged by MIBI-TOF or single-plex immunohistochemistry (IHC) over 12 days. Pixel-level features were highly concordant across all 16 targets assessed in both staining intensity (R2 = 0.94 ± 0.04) and frequency (R2 = 0.95 ± 0.04). Comparison to digitized, single-plex IHC on adjacent serial sections revealed similar concordance (R2 = 0.85 ± 0.08) as well. Lastly, automated segmentation and clustering of eight cell populations found that cell frequencies between replicates yielded an average correlation of R2 = 0.92 ± 0.06. Taken together, we demonstrate that MIBI-TOF, with well-vetted reagents and automated analysis, can generate consistent and quantitative annotations of clinically relevant cell states in archival human tissue, and more broadly, present a scalable framework for benchmarking multiplexed IHC approaches.
Liu, et al., Lab. Invest. March 2022
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41374-022-00778-8
The immunoregulatory landscape of human tuberculosis granulomas <span class='publication-meta'>McCaffrey, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Nature Immunology</i> February 2022</span>
Abstract: Tuberculosis (TB) in humans is characterized by formation of immune-rich granulomas in infected tissues, the architecture and composition of which are thought to affect disease outcome. However, our understanding of the spatial relationships that control human granulomas is limited. Here, we used multiplexed ion beam imaging by time of flight (MIBI-TOF) to image 37 proteins in tissues from patients with active TB. We constructed a comprehensive atlas that maps 19 cell subsets across 8 spatial microenvironments. This atlas shows an IFN-γ-depleted microenvironment enriched for TGF-β, regulatory T cells and IDO1+ PD-L1+ myeloid cells. In a further transcriptomic meta-analysis of peripheral blood from patients with TB, immunoregulatory trends mirror those identified by granuloma imaging. Notably, PD-L1 expression is associated with progression to active TB and treatment response. These data indicate that in TB granulomas, there are local spatially coordinated immunoregulatory programs with systemic manifestations that define active TB.
McCaffrey, et al., Nature Immunology February 2022
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-021-01121-x
Transition to invasive breast cancer is associated with progressive changes in the structure and composition of tumor stroma <span class='publication-meta'>Risom, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Cell</i> January 2022</span>
Abstract: Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a pre-invasive lesion that is thought to be a precursor to invasive breast cancer (IBC). To understand the changes in the tumor microenvironment (TME) accompanying transition to IBC, we used multiplexed ion beam imaging by time of flight (MIBI-TOF) and a 37-plex antibody staining panel to interrogate 79 clinically annotated surgical resections using machine learning tools for cell segmentation, pixel-based clustering, and object morphometrics. Comparison of normal breast with patientmatched DCIS and IBC revealed coordinated transitions between four TME states that were delineated based on the location and function of myoepithelium, fibroblasts, and immune cells. Surprisingly, myoepithelial disruption was more advanced in DCIS patients that did not develop IBC, suggesting this process could be protective against recurrence. Taken together, this HTAN Breast PreCancer Atlas study offers insight into drivers of IBC relapse and emphasizes the importance of the TME in regulating these processes.
Risom, et al., Cell January 2022
doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.023
Multiplexed Ion Beam Imaging: Insights into Pathobiology <span class='publication-meta'>Liu, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Annual Review of Pathology</i> 2022</span>
Abstract: Next-generation tools formultiplexed imaging have driven a new wave of innovation in understanding how single-cell function and tissue structure are interrelated. In previous work, we developed multiplexed ion beam imaging by time of flight, a highly multiplexed platform that uses secondary ion mass spectrometry to image dozens of antibodies tagged with metal reporters. As instrument throughput has increased, the breadth and depth of imaging data have increased as well. To extract meaningful information from these data, we have developed tools for cell identification, cell classification, and spatial analysis. In this review, we discuss these tools and provide examples of their application in various contexts, including ductal carcinoma in situ, tuberculosis, and Alzheimer’s disease.We hope the synergy between multiplexed imaging and automated image analysis will drive a new era in anatomic pathology and personalized medicine wherein quantitative spatial signatures are used routinely for more accurate diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic selection.
Liu, et al., Annual Review of Pathology 2022
doi: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-030321-091459
Signatures of plasticity, metastasis, and immunosuppression in an atlas of human small cell lung cancer<span class='publication-meta'>Chan, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Cancer Cell</i> October 2021</span>
Abstract: Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive malignancy that includes subtypes defined by differential expression of ASCL1, NEUROD1, and POU2F3 (SCLC-A, -N, and -P, respectively). To define the heterogeneity of tumors and their associated microenvironments across subtypes, we sequenced 155,098 transcriptomes from 21 human biospecimens, including 54,523 SCLC transcriptomes. We observe greater tumor diversity in SCLC than lung adenocarcinoma, driven by canonical, intermediate, and admixed subtypes. We discover a PLCG2-high SCLC phenotype with stem-like, pro-metastatic features that recurs across subtypes and predicts worse overall survival. SCLC exhibits greater immune sequestration and less immune infiltration than lung adenocarcinoma, and SCLC-N shows less immune infiltrate and greater T cell dysfunction than SCLC-A. We identify a profibrotic, immunosuppressive monocyte/macrophage population in SCLC tumors that is particularly associated with the recurrent, PLCG2-high subpopulation.
Chan, et al., Cancer Cell October 2021
doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2021.09.008
Multiplexed imaging reveals an IFN-γ-driven inflammatory state in nivolumab-associated gastritis<span class='publication-meta'>Ferrian, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Cell Reports Medicine</i> October 2021</span>
Abstract: Immune checkpoint blockade using PD-1 inhibition is an effective approach for treating a wide variety of cancer subtypes. While lower gastrointestinal (GI) side effects are more common, upper gastrointestinal adverse events are rarely reported. Here, we present a case of nivolumab-associated autoimmune gastritis. To elucidate the immunology underlying this condition, we leverage multiplexed ion beam imaging by time-of-flight (MIBI-TOF) to identify the presence and proportion of infiltrating immune cells from a single section of biopsy specimen. Using MIBI-TOF, we analyze formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human gastric tissue with 28 labels simultaneously. Our analyses reveal a gastritis characterized by severe mucosal injury, interferon gamma (IFN-γ)-producing gastric epithelial cells, and mixed inflammation that includes CD8 and CD4 T cell infiltrates with reduced expression of granzyme B and FOXP3, respectively. Here, we provide a comprehensive multiplexed histopathological mapping of gastric tissue, which identifies IFN-γ-producing epithelial cells as possible contributors to the nivolumab-associated gastritis.
Ferrian, et al., Cell Reports Medicine October 2021
doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100419
Spatio-temporal coordination at the maternal-fetal interface promotes trophoblast invasion and vascular remodeling in the first half of human pregnancy<span class='publication-meta'>Greenbaum, <i>et al.</i>, <i>BioRxiv</i> September 2021</span>
Abstract:Beginning in the first trimester, fetally derived extravillous trophoblasts (EVTs) invade the uterus and remodel its spiral arteries, transforming them into large, dilated blood vessels that lack smooth muscle and are partially lined with EVTs instead of vascular endothelium. Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain how EVTs coordinate with decidual cells to promote a tissue microenvironment conducive to spiral artery remodeling (SAR). However, it remains a matter of debate which immune and stromal cell types participate in these interactions, how this process evolves with respect to gestational age, and which anatomic routes are the predominate path of EVT invasion in humans. To elucidate this complex interplay, we used multiplexed ion beam imaging by time of flight with a 37-plex antibody panel to build the first spatio-temporal atlas of the human maternal-fetal interface in the first half of pregnancy at single-cell resolution. We analyzed ~500,000 cells and 588 spiral arteries within intact decidua from 66 patients between 6-20 weeks of gestation. Using custom machine learning algorithms for cell segmentation and classification, we evaluated the spatial distributions and phenotype of 20 maternal and five EVT populations with respect to gestational age and SAR. Gestational age substantially influenced the frequency of most maternal immune and stromal cells, with tolerogenic subsets expressing CD206, CD163, TIM-3, Galectin-9, and IDO-1 preferentially enriched at later time points. In contrast, SAR progression, and not gestational age, preferentially correlated with local invasion of EVTs. Lastly, by comparing spatial co-occurrence and phenotype of decidual interstitial, perivascular and intravascular EVTs with respect to SAR progression, we developed a statistical model suggesting an intravasation mechanism as the predominant route of EVT invasion in superficial decidua. Taken together, these results support a coordinated model of decidualization in which increasing gestational age drives a transition in maternal decidua towards a tolerogenic niche conducive to locally regulated, EVT-dependent SAR.
Greenbaum, et al., BioRxiv September 2021
doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.09.08.459490
Subcellular localization of biomolecules and drug distribution by high-definition ion beam imaging<span class='publication-meta'>Rovira-Clavé, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Nature Communications</i> July 2021</span>
Abstract: Simultaneous visualization of the relationship between multiple biomolecules and their ligands or small molecules at the nanometer scale in cells will enable greater understanding of how biological processes operate. We present here high-definition multiplex ion beam imaging (HD-MIBI), a secondary ion mass spectrometry approach capable of high-parameter imaging in 3D of targeted biological entities and exogenously added structurally-unmodified small molecules. With this technology, the atomic constituents of the biomolecules themselves can be used in our system as the “tag” and we demonstrate measurements down to ~30 nm lateral resolution. We correlated the subcellular localization of the chemotherapy drug cisplatin simultaneously with five subnuclear structures. Cisplatin was preferentially enriched in nuclear speckles and excluded from closed-chromatin regions, indicative of a role for cisplatin in active regions of chromatin. Unexpectedly, cells surviving multi-drug treatment with cisplatin and the BET inhibitor JQ1 demonstrated near total cisplatin exclusion from the nucleus, suggesting that selective subcellular drug relocalization may modulate resistance to this important chemotherapeutic treatment. Multiplexed high-resolution imaging techniques, such as HD-MIBI, will enable studies of biomolecules and drug distributions in biologically relevant subcellular microenvironments by visualizing the processes themselves in concert, rather than inferring mechanism through surrogate analyses.
Rovira-Clavé, et al., Nature Communications July 2021
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24822-1
On Clustering for Cell Phenotyping in Multiplex Immunohistochemistry (mIHC) and Multiplexed Ion Beam Imaging (MIBI) Data<span class='publication-meta'>Seal, <i>et al.</i>, <i>Research Square</i> July 2021</span>
Results: Unsupervised cell phenotyping methods including PhenoGraph, flowMeans, and SamSPECTRAL, primarily used in flow cytometry data, often perform poorly or need elaborate tuning to perform well in the context of mIHC and MIBI data. We show that, instead, semi-supervised cell clustering using Random Forests, linear and quadratic discriminant analysis are superior. We test the performance of the methods on two mIHC datasets from the University of Colorado School of Medicine and a publicly available MIBI dataset. Each dataset contains numerous highly complex images.
Seal, et al., Research Square July 2021
doi: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-609920/v1
Multiplexed single-cell metabolic profiles organize the spectrum of cytotoxic human T cells<span class='publication-meta'>Hartmann, <i>et al., Nat. Biotechnology</i> Aug 2020</span>
Hartmann, et al., Nat. Biotechnol. 31 Aug 2020: s41587-020-0651-8
doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0651-8
Multimodal analysis of composition and spatial architecture in human squamous cell carcinoma<span class='publication-meta'>Ji, <i>et al., Cell</i> Jul 2020</span>
Ji, et al., Cell (2020) July 23
Multiplexed imaging of human tuberculosis granulomas uncovers immunoregulatory features conserved across tissue and blood<span class='publication-meta'>McCaffrey, <i>et al., BioRxiv</i> Jun 2020</span>
PREPRINT – McCaffrey, et al., BioRxiv (2020) June 09
MIBI-TOF: A multiplexed imaging platform relates cellular phenotypes and tissue structure<span class='publication-meta'>Keren, <i>et al., Science Advances</i> Oct 2019</span>
Abstract: Understanding tissue structure and function requires tools that quantify the expression of multiple proteins while preserving spatial information. Here, we describe MIBI-TOF (multiplexed ion beam imaging by time of flight), an instrument that uses bright ion sources and orthogonal time-of-flight mass spectrometry to image metal-tagged antibodies at subcellular resolution in clinical tissue sections. We demonstrate quantitative, full periodic table coverage across a five-log dynamic range, imaging 36 labeled antibodies simultaneously with histochemical stains and endogenous elements. We image fields of view up to 800 μm × 800 μm at resolutions down to 260 nm with sensitivities approaching single-molecule detection. We leverage these properties to interrogate intrapatient heterogeneity in tumor organization in triple-negative breast cancer, revealing regional variability in tumor cell phenotypes in contrast to a structured immune response. Given its versatility and sample back-compatibility, MIBI-TOF is positioned to leverage existing annotated, archival tissue cohorts to explore emerging questions in cancer, immunology, and neurobiology.
Keren, et al., Science Advances 09 Oct 2019: 5(10), eaax5851
Tissue imaging by mass spectrometry: a practical guide for the medicinal chemist<span class='publication-meta'>Johnson, <em>et al., ACS Medical Chemistry Letters</em> Jan 2019</span>
Johnson et al. ACS Medical Chemistry Letters. January, 2019
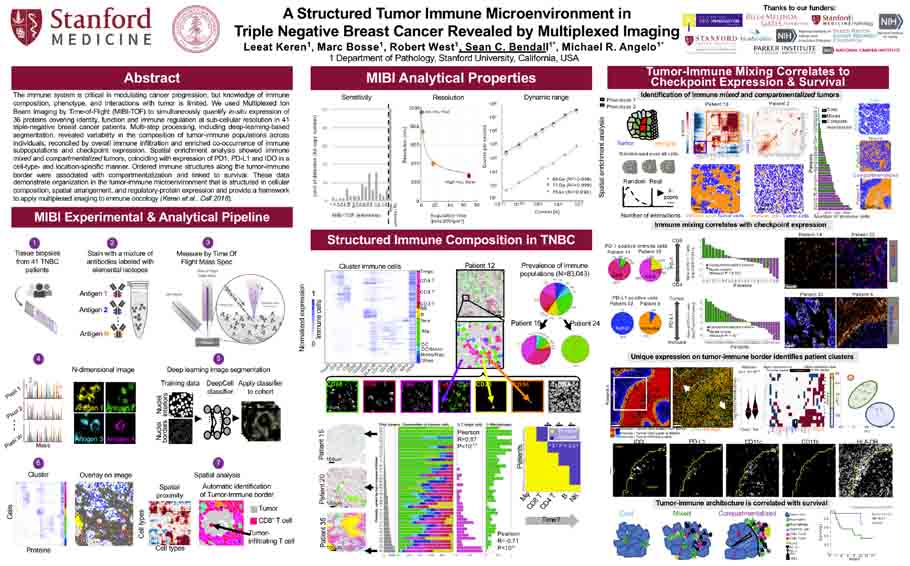
A structured tumor-immune microenvironment in triple negative breast cancer revealed by multiplexed ion beam imaging<span class='publication-meta'>Keren, <em>et al, Cell</em> Sept 2018</span>
Keren et al. Cell, Volume 174, Issue 6, P1373-1387. E19. September 06, 2018
Multiplexed ion beam imaging analysis for quantitation of protein expression in cancer tissue sections<span class='publication-meta'>Rost, <em>et al., Lab. Invest.</em> Aug 2017</span>
Rost et al., Lab Invest. 2017 Aug;97(8):992-1003
SITC 2022 - #89
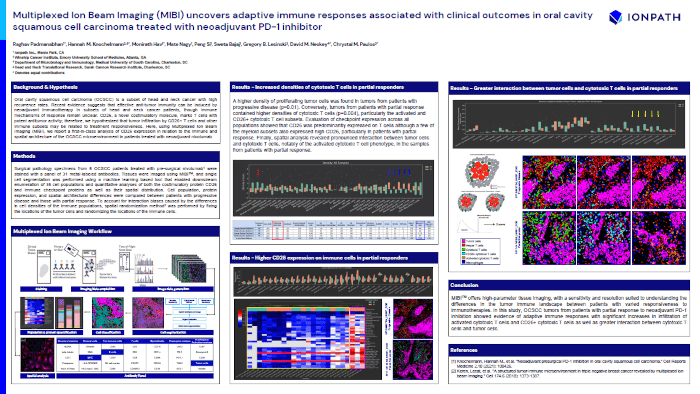
Multiplexed Ion Beam Imaging (MIBI) uncovers adaptive immune responses associated with clinical outcomes in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma treated with neoadjuvant PD-1 inhibitor
SITC 2022 - #1294
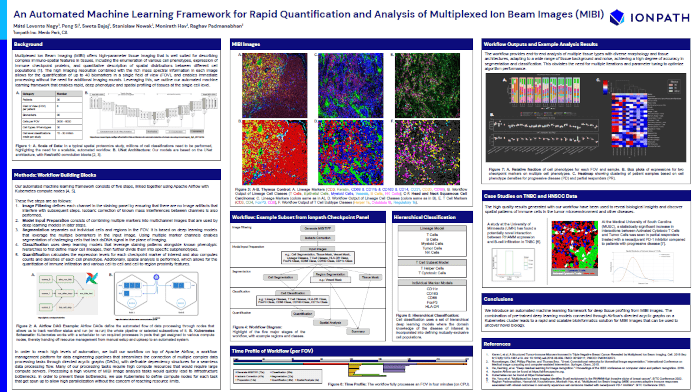
An Automated Machine Learning Framework for Rapid Quantification and Analysis of Multiplexed Ion Beam Images (MIBI)
SITC 2021
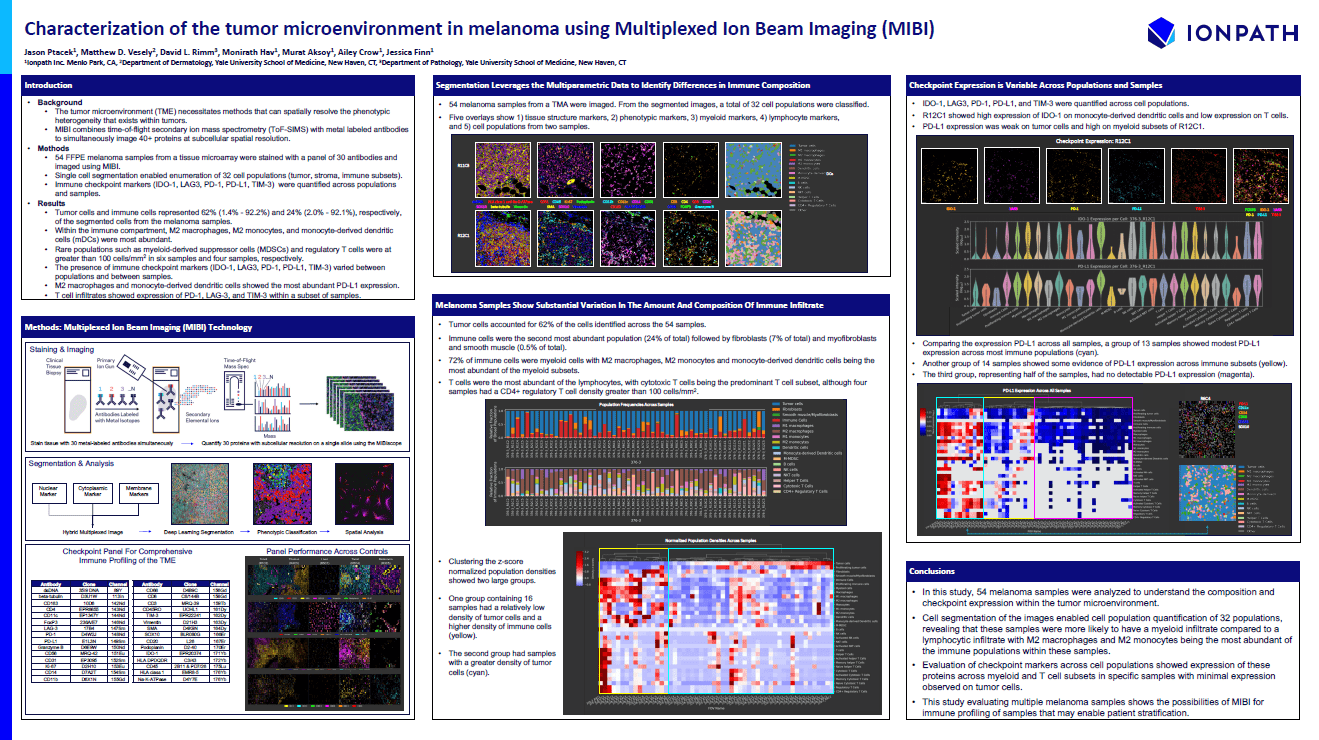
Characterization of the Tumor Microenvironment in Melanoma Using Multiplexed Ion Beam Imaging (MIBI)
SITC 2020 - P48
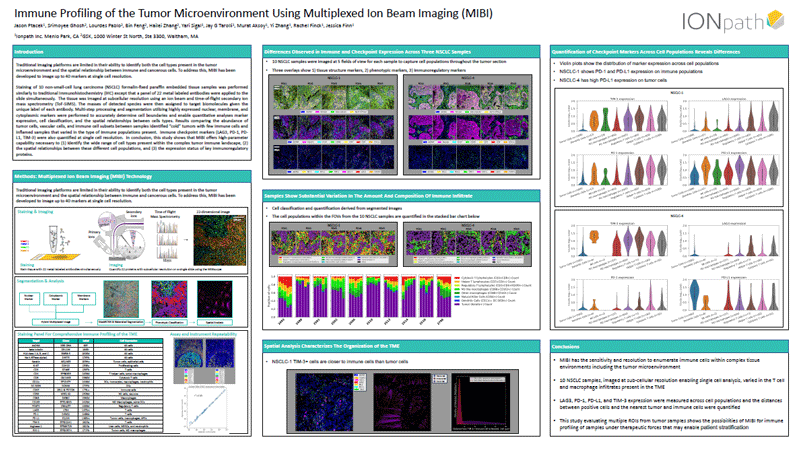
Advances in Multiplexed Ion Beam Imaging (MIBI) for immune profiling of the tumor microenvironment
SITC 2019 - P61
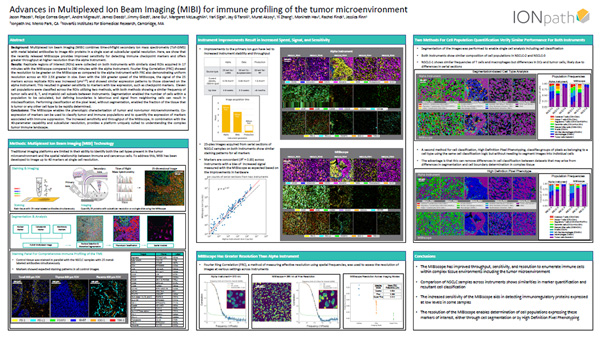
Segmentation and Classification of Single Cells using Multiplexed Ion Beam Imaging (MIBI)
SITC 2018 - P106
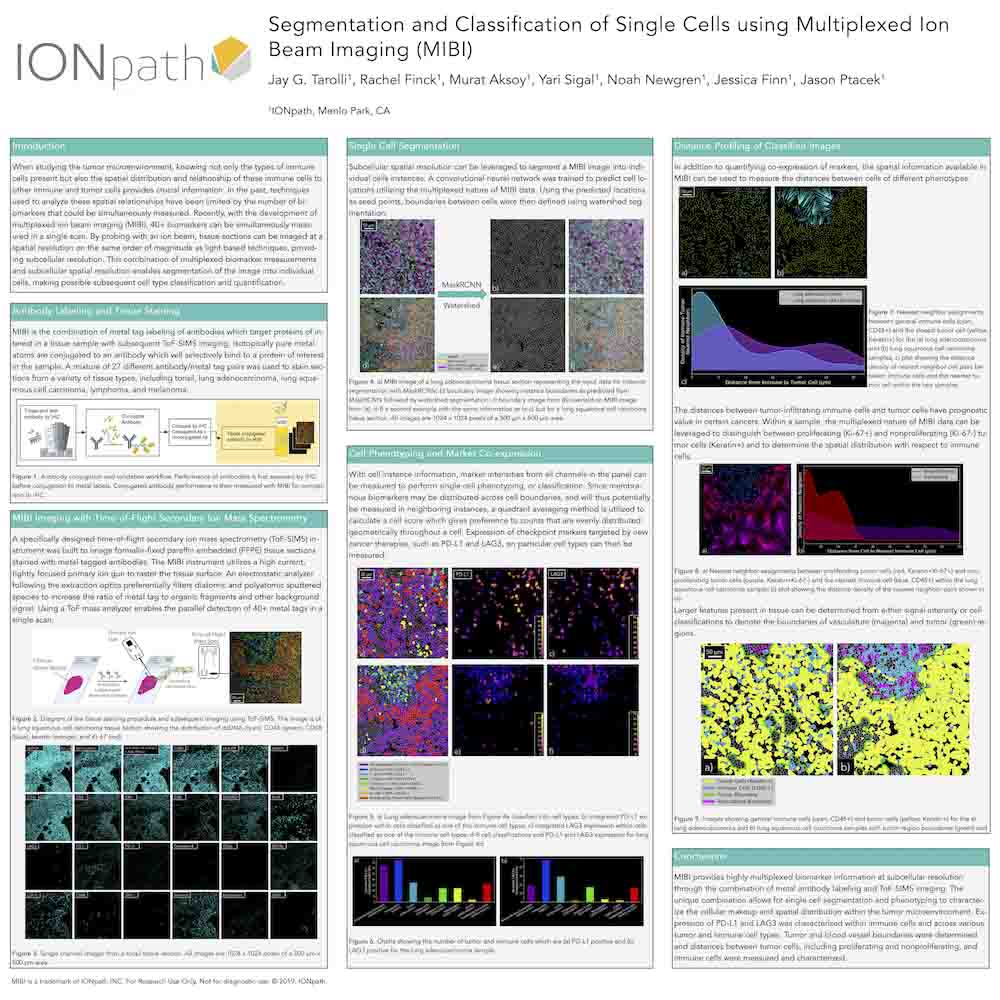
Multiplexed Ion Beam Imaging For Characterization of the Tumor Microenvironment Across Tumor Types
SITC 2018 - P20
A Structured Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Revealed by Multiplexed Imaging