How MIBI Technology Reveals Key Elements of the Tumor Microenvironment |SITC 2020 Poster
Highlights from the poster
If you’re not familiar with IONpath’s technology, a quick introduction is in order before we review the poster. We use multiplexed ion beam imaging (MIBI™) technology as the foundation for our spatial proteomic platform, which was designed to fit easily into a pathologist’s workflow. MIBI technology pairs time-of-flight mass spectrometry with metal-tagged antibodies to detect the presence of more than 40 proteins in a single tissue scan. Results are spatially resolved down to the subcellular level to give scientists a deeper understanding of tissue architecture, biological microenvironments, expression of key immunoregulatory proteins, and more.
In the SITC poster, our team reported results from applying our MIBI imaging technology to the tumor microenvironment for the detection of immune checkpoint markers in samples of non-small cell lung cancer. Results highlighted the platform’s evolution from alpha and beta instruments to the current instrument, the MIBIscope, a tool with significantly improved performance in sample throughput, sensitivity, and resolution.
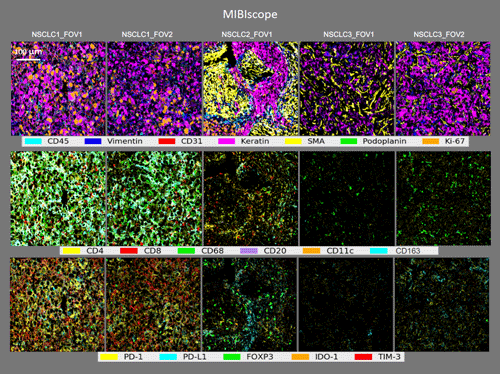
Profiling the tumor microenvironment of NSCLC
Researchers were able to segment individual cells and, using a set of phenotypic rules of marker expression, classify more than 20 cell populations in the regions of interest, including tumor cells, myeloid cell subsets, and B and T immune cells. They also calculated the number of cells in each population, and even classified signals down to the pixel level for rapid, accurate quantification of cell population densities without the need for segmentation techniques. The high sensitivity of the platform allowed for the detection of proteins expressed at very low levels in the samples, and the multiplexing capacity made it possible to evaluate co-expression patterns that may be relevant for mechanisms such as immune suppression.
As the poster concludes, “The increased sensitivity and throughput of the MIBIscope, in combination with the 40-parameter capability and subcellular resolution, provides a platform uniquely suited to understanding the complex tumor immune landscape.”