SITC 2021: Posters Detail Use of MIBI Technology for Immunotherapy Studies
Characterizing the melanoma tumor microenvironment
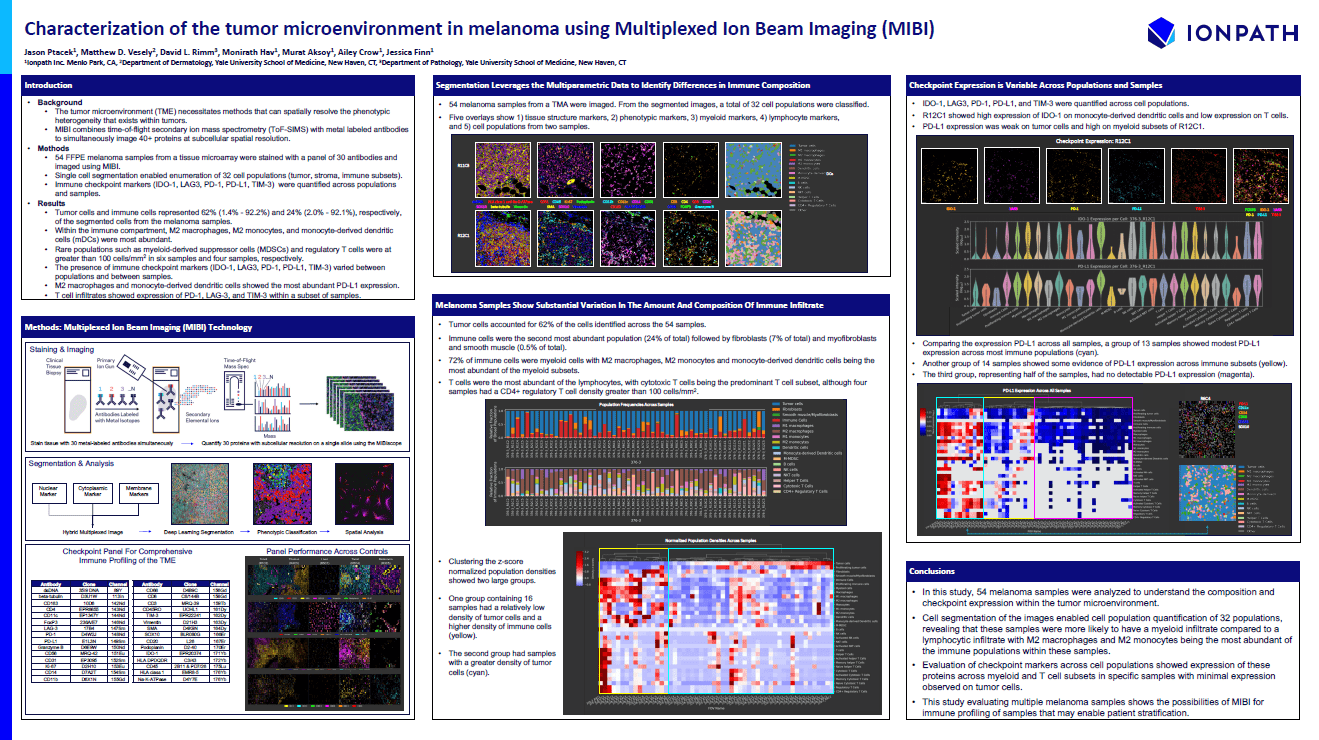
A poster from scientists at Ionpath and Yale University School of Medicine illustrates a project focused on melanoma in which spatial resolution of protein data provided new understanding of the tumor microenvironment and checkpoint expression in various cell types and populations.
In this project, scientists analyzed 54 melanoma samples taken from FFPE blocks, looking for 30 different proteins using MIBI technology. They used the resulting data to segment and classify individual cells, identifying 32 cell populations and quantifying immune checkpoint markers across each of them.
Immunotherapy validation
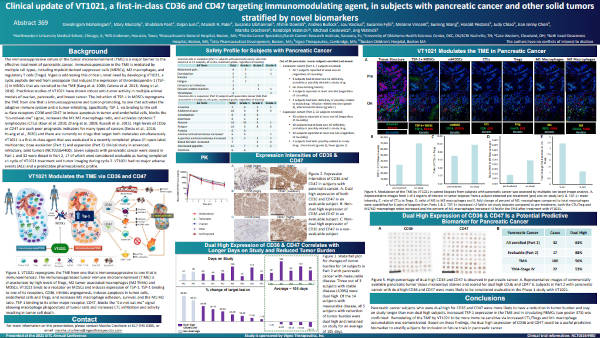
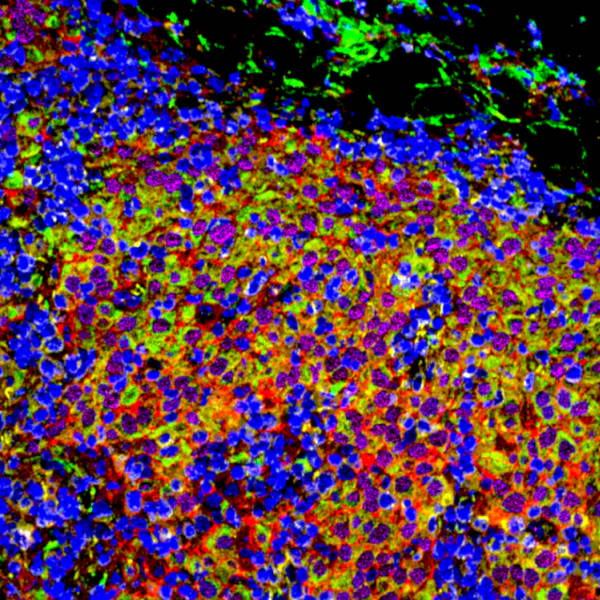
Separately, scientists at Northwestern University, MD Anderson, and other cancer centers reported results from clinical studies of VT1021, a cyclic peptide under development by Vigeo Therapeutics for the treatment of various types of cancer. The treatment aims to reduce the immunosuppressive environment around the tumor, making it easier to kill cancer cells. In studies of patients with pancreatic cancer, researchers used MIBI technology to study how the treatment alters the tumor microenvironment. As described in their poster, they found that patients with high CD36 and CD47 counts were more likely to have their tumors shrink, and that remodeling of the tumor microenvironment did occur.
We’re delighted to see continued evidence of the value of MIBI technology for immunotherapy studies, and look forward to seeing results from more customers at future conferences.